What is AI
Artificial intelligence (AI) is exciting, powerful, and game changing. The mainstream hype machine has generated gale-force winds behind its sail, to the point that AI is on virtually everyone’s radar and is part of the vernacular and yet is barely understood by the majority of people.
Introduction
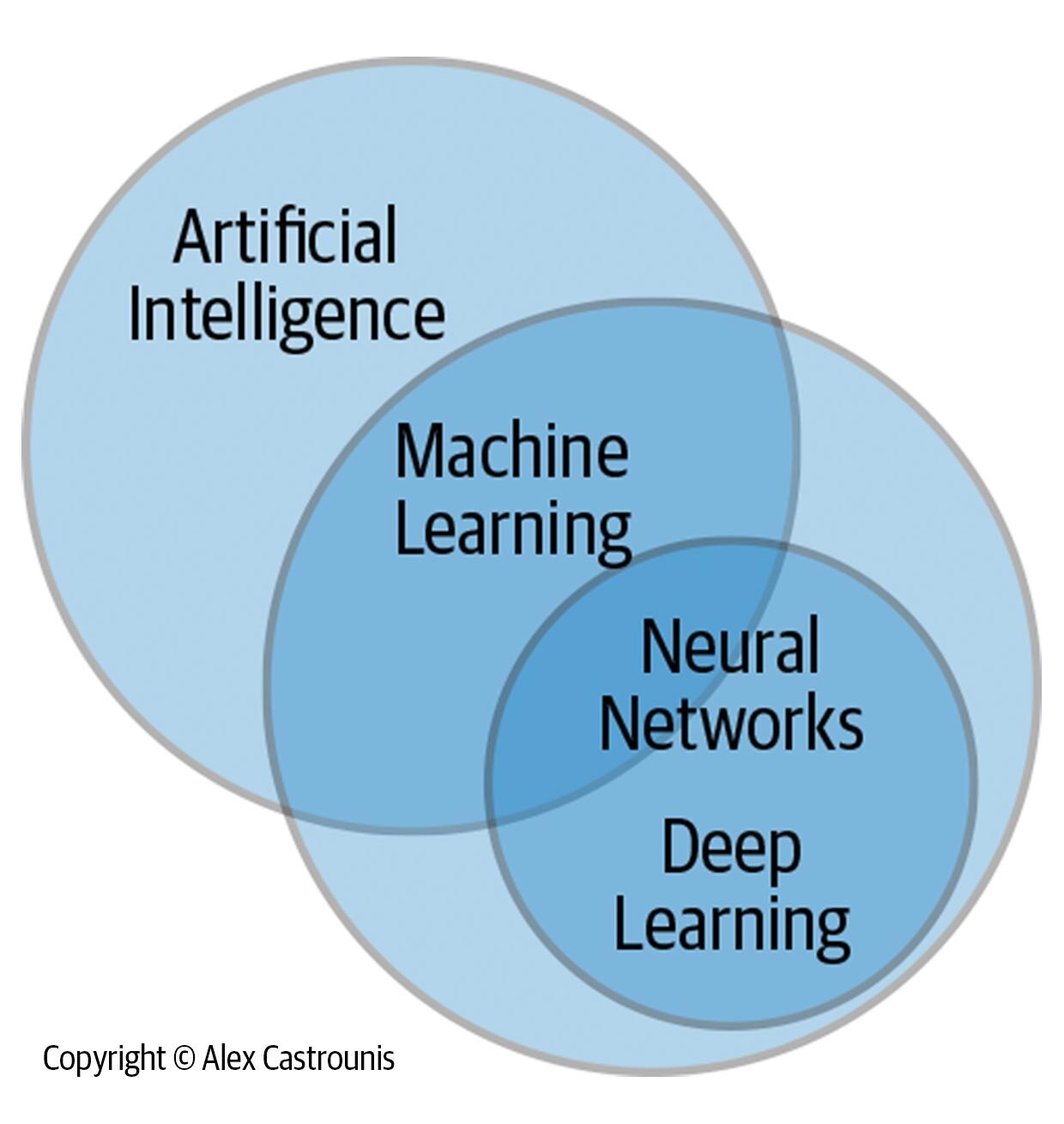
AI is a set of concepts, tools, and techniques that represents huge disruptive and transformative potential. Definition-wise, we can think of AI simply as intelligence exhibited by machines that can be used in a beneficial way (e.g., carrying out tasks, making decisions, assisting humans, saving lives). More specifically, AI describes when a machine is able to learn from information (data), generate some degree of understanding, and then use the knowledge learned to do something. AI includes machine learning and specific techniques such as deep learning as subsets.
The field of AI is related to and draws from aspects of neuroscience, psychology, philosophy, mathematics, statistics, computer science, computer programming, and more. AI is also sometimes referred to as machine intelligence or cognitive computing given its foundational basis and relationship to cognition; that is, the mental processes associated with developing knowledge and comprehension.
So what powers intelligence? In the case of humans and animals, new information is constantly collected from experience and the surrounding environment through the five senses. For AI applications, the answer is information in the form of data.
Experience factors heavily into AI, as well. AI is made possible by a training and optimization process that uses relevant data for a given task. AI applications can be updated and improved over time as new data becomes available, and this is the learning-from-experience aspect of AI.
Ultimately, data and the models trained from it can become stale, a phenomena referred to as model drift. It is therefore critical that any applications of AI are refreshed and continue to gain experience and knowledge through continued learning from new data.
Key Historical Events and Milestones
The evolution of artificial intelligence has been marked by several key historical events and milestones that have shaped the field into what it is today.
In 1950, Alan Turing's publication of "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" posed the fundamental question of whether machines can think, leading to the famous Turing Test.
Then, in 1956, John McCarthy coined the term "artificial intelligence" at the groundbreaking AI conference at Dartmouth College, where the first running AI software program, the Logic Theorist, was created.
A pivotal moment came in 1967 when Frank Rosenblatt developed the Mark 1 Perceptron, a computer based on a neural network that learned through trial and error.
The 1980s saw the rise of neural networks using backpropagation algorithms for training, significantly advancing AI applications. The publication of "Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach" by Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig in 1995 became a seminal textbook in the study of AI.
In 1997, IBM's Deep Blue made history by defeating world chess champion Garry Kasparov, showcasing the power of AI in specialized tasks. This victory made a significant mark in the history of AI as it showcased the potential of machine intelligence to compete and excel in complex strategic games against human champions. The event not only demonstrated the advancements in AI technology but also highlighted the possibilities of leveraging such systems for challenging intellectual tasks.
John McCarthy, in 2004, further contributed to the field with his defining paper on artificial intelligence. Significant progress was made in 2011 when IBM's Watson triumphed over human champions on Jeopardy!, demonstrating AI's ability to excel in natural language processing.
The year 2015 saw Baidu's Minwa supercomputer employing convolutional neural networks for image recognition with unprecedented accuracy.
In 2016, DeepMind's AlphaGo defeated the world champion Go player Lee Sodol, showcasing AI's ability to navigate complex decision-making processes. Recent advancements in large language models, like ChatGPT, have been driving significant performance improvements in AI and its potential for creating value in various industries.
The Advantages and Benefits of AI
Making decisions and taking action based solely on historical precedent, simple analytics, and gut feel no longer gets the job done—nor does pursuing near-sighted goals or commoditized technologies. And yet, too many businesses remain mired in the status quo. More and more, it’s those that effectively use analytics who succeed; that is, those that extract information such as patterns, trends, and insights from data in order to make decisions, take actions, and produce outcomes. This includes both traditional analytics and advanced analytics, which are complementary. Also, AI allows humans to use analytics in ways they would otherwise not be able to on their own.
Data is a core advantage if, and only if, you know how to use it. Most companies should begin to think of themselves as data and analytics companies, regardless of what their core offerings are. As long as data is involved, this is a critical step in getting ahead of the competition while also gaining an increased ability to create huge benefits for both people and business.
Some highly beneficial and advanced applications of AI include helping blind and visually disabled people “see” and cardiovascular disease assessment and prediction of risk factors from retinal scan images.
Applied AI
The term applied ai is intended to distinguish between theoretical AI and AI that is applied to real-world use cases, something for which we’re now seeing a significant and diverse proliferation. I call the change that many companies are undergoing an applied AI transformation when they harness AI to generate certain benefits or outcomes not attainable through other methods, or in other cases, to produce high-impact outcomes much more efficiently (time and cost) and with greater value.
Use Case - Weather Forecasting Models
Machine-learning techniques play a crucial role in enhancing weather forecasting models by increasing their applicability and precision. By incorporating machine-learning algorithms, these models are able to analyze vast amounts of data more effectively, identifying complex patterns and relationships that may not be easily recognized using traditional methods. This allows weather forecasters to make more accurate predictions and provide more detailed and reliable information to the public. Additionally, machine-learning techniques enable the models to continuously learn and adapt to changing conditions, improving their overall performance and making them better equipped to handle the inherent uncertainties in weather forecasting.
Conclusion
AI is game changing and rapidly advancing in its capabilities. It’s being applied more than ever in new and innovative ways that can benefit both people and businesses alike. To learn more, check out my book, AI for People and Business.